Disable inter-container communication
April 1, 2022 • By Andy Rea
6 min readTL;DR;
Here I learn how the --link arg is now legacy and that icc=false is a recommended security practice as it disables communications on the default bridge network. To allow containers to communicate with icc=false you need to use custom networks.
Longer version
Disabling inter-container communication (icc) forces any containers to have explicit links with those it needs to communicate with. This is a setting on the docker daemon itself and the setting can be applied in the systemd configuration.
To setup this example I have created a toy app called todos with very simple functionality. I have split the project into two containers:
- The Proxy - this is the existing work with nginx
- The Todos App - this is a small go app to create, update and list todos
The idea is that there will be two container instances running - one for nginx and one for the todo app; a custom config is then supplied to nginx to proxy all calls to the todos app. The nginx container instance will be the only one with any port mappings.
I wont detail all the code for the sample app or the nginx configuration, that can be found in the repository here https://github.com/reaandrew/nginx-security
Setting up the two container instances
I have updated the Makefile to include the todos container.
.PHONY: build
build:
docker build -t reaandrew/nginx-secure ./proxy
(cd todos && go build -o todos main.go)
docker build -t reaandrew/todos-secure ./todos
.PHONY: run
run: build
docker run --name todos-secure --read-only \
-d -t reaandrew/todos-secure
docker run --name nginx-secure --read-only \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/proxy_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/client_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/fastcgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/uwsgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/scgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/nginx,tmpfs-size=1m \
--link todos-secure:todos \
-d -p 8080:8080 -t reaandrew/nginx-secure
.PHONY: kill
kill:
docker kill nginx-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker rm nginx-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker kill todos-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker rm todos-secure 2> /dev/null || :
.PHONY: logs
logs:
docker logs nginx-secure
docker logs todos-secure
The important part is the addition of an explicit link --link todos-secure:todos. This allows the nginx container to reference a host name of todos which you can see in the following nginx config snippet:
Later on I update this as this doesnt work when icc=false and is actually now a legacy approach.
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://todos:8080;
}
...
Also note that no ports have been exposed for the todos app, only the nginx container.
Testing out the ICC switch
Before disabling ICC
To test this I am shelling into a busybox container and trying to consume the todos app directly, not via the nginx container.
Refresh the containers, kill and re-run.
make kill
make run
Review the containers which are running:
> docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
da33f3a2bf52 reaandrew/nginx-secure "/usr/sbin/nginx -g …" 43 seconds ago Up 42 seconds 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, :::8080->8080/tcp nginx-secure
2b7afded4cdf reaandrew/todos-secure "/usr/bin/todos" 43 seconds ago Up 42 seconds todos-secure
I want to start a new container which has a shell and some tools so I can test out inter container communication without using explcit links. Before I do this I need to know what the IP is of the todo container.
> docker inspect todos-secure | jq -r '.[]|.NetworkSettings.Networks.bridge.IPAddress'
172.17.0.2
Now I have the IP I can start the other container, shell in and try to consume the todos list endpoint which should return an empty array.
> docker run -it --rm busybox
> wget -qO- 172.17.0.2:8080/todos
[]
Success, this shows we can communicate between containers, but I want to disable this.
After disabling ICC
To disable the inter-container communication you need to add an argument to the docker systemd file /lib/systemd/system/docker.service (the location may be different on your setup.) The ExecStart line from that file should look like the following:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd --icc=false -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Now reload the systemd daemon since the content of the file has changed and restart the docker daemon.
> sudo systemctl daemon-reload
> sudo systemctl restart docker
Now when I try to consume the todos from the busybox I am expecting the process to hang since the inter-container communication has been disabled, but for the demo I will set a timeout to show it failing.
> make kill
> make run
> docker inspect todos-secure | jq -r '.[]|.NetworkSettings.Networks.bridge.IPAddress'
172.17.0.2
> docker run -it --rm busybox
> wget -T 2 -qO- 172.17.0.2:8080/todos
wget: download timed out
Now hitting the todos API from the host, the way it is intended to be used is also hanging!!
> curl -m 2 -v localhost:8080/todos
* Trying 127.0.0.1:8080...
* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 8080 (#0)
> GET /todos HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8080
> User-Agent: curl/7.74.0
> Accept: */*
>
* Operation timed out after 2003 milliseconds with 0 bytes received
* Closing connection 0
curl: (28) Operation timed out after 2003 milliseconds with 0 bytes received
THIS DOESN’T WORK!!!
How to fix this and keep Inter-Container Communication disabled?
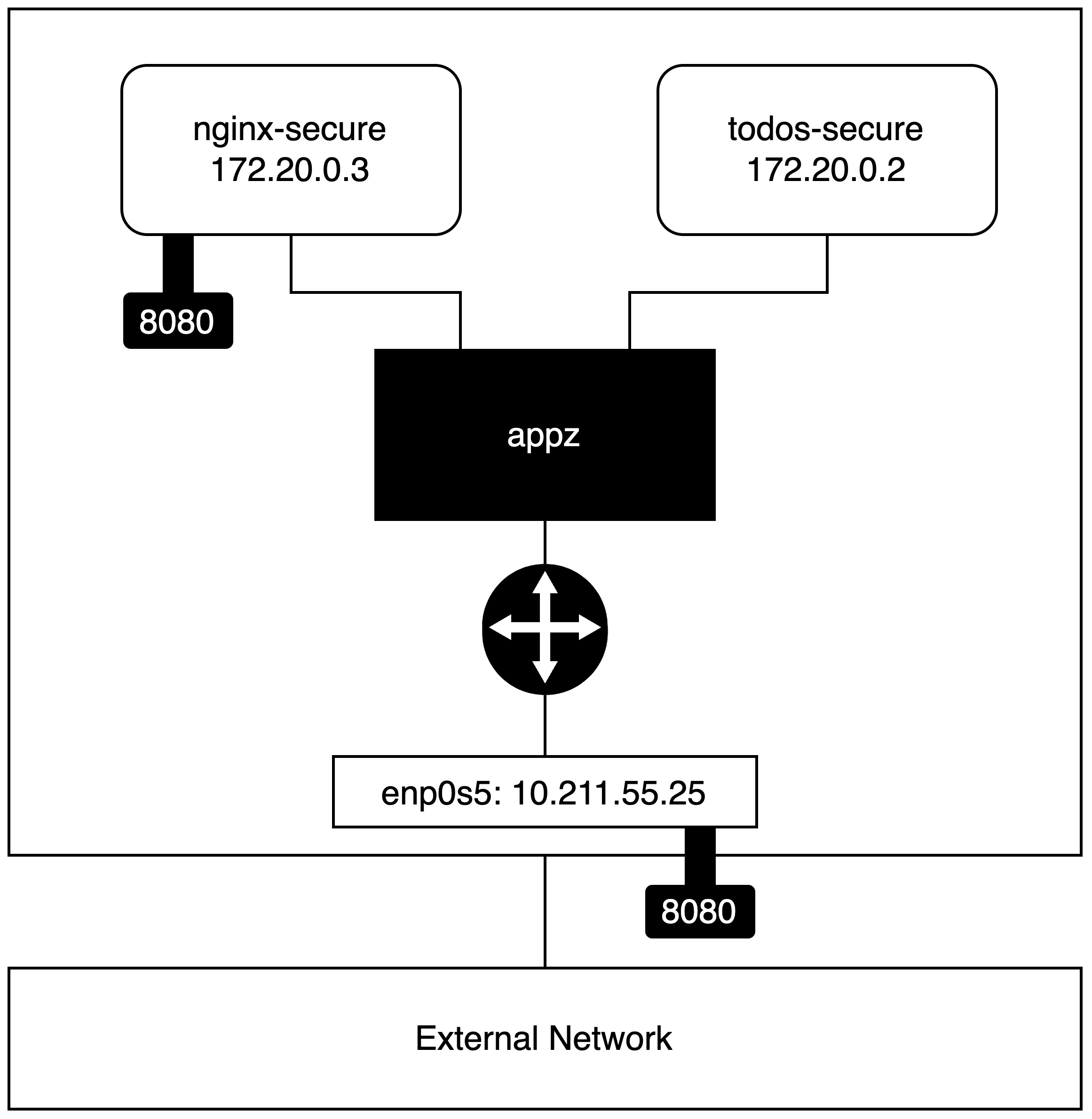
Turns out --link is now legacy along with the default bridge which I have used above. The recomendation now is to use user-defined networks with docker including (for this example) user-defined bridges. So the final steps are to create a custom bridge network, attach the two containers and see if the todos api can be consumed from the host.
Here is the update Makefile:
.PHONY: build
build:
docker build -t reaandrew/nginx-secure ./proxy
(cd todos && go build -o todos main.go)
docker build -t reaandrew/todos-secure ./todos
.PHONY: run
run: build
docker network create --driver bridge appz
docker run --name todos-secure --read-only \
--network appz \
-d -t reaandrew/todos-secure
docker run --name nginx-secure --read-only \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/proxy_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/client_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/fastcgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/uwsgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/scgi_temp,tmpfs-size=2m \
--mount type=tmpfs,destination=/tmp/nginx,tmpfs-size=1m \
--network appz \
-d -p 8080:8080 -t reaandrew/nginx-secure
.PHONY: kill
kill:
docker kill nginx-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker rm nginx-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker kill todos-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker rm todos-secure 2> /dev/null || :
docker network rm appz 2> /dev/null || :
.PHONY: logs
logs:
docker logs nginx-secure
docker logs todos-secure
The changes to the Makefile include:
- Create the network Also update the kill target to remove the network
- Remove the
--linkfrom the nginx container and instead attach both containers to the newappznetwork.
The other change required is the hostname which nginx uses to reference the upstream service. Before I defined this as todos but now this has changed to the name given to the container todos-secure.
The updated block in the nginx configuration file is now:
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://todos-secure:8080;
}
...
Finally!
And now when the endpoint is hit from the host we get the correct response.
> make kill
> make run
> curl -m 2 -v localhost:8080/todos
[]